RudderStack's Airflow Provider lets you programmatically schedule and trigger your Reverse ETL syncs from outside RudderStack and integrate them with your existing Airflow workflows.
For more information on the codebase and sample implementation, refer to our GitHub Repository.
Using the Airflow Provider
To use the Airflow Provider, you must have a working Apache Airflow installation. For more information, refer to the Airflow documentation.
Follow the steps in the below sections to use the RudderStack Airflow Provider:
Running Airflow
Initialize all the dependencies by running Apache Airflow via the following command:
airflow standaloneInstalling Airflow Provider
Install the RudderStack Airflow Provider by running the following command:
pip install rudderstack-airflow-providerCreating an Airflow connection
To create a new Airflow connection, follow these steps:
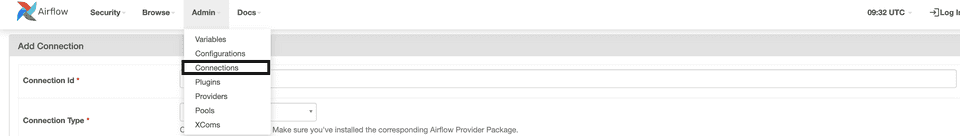
- In your Airflow dashboard, go to Admin > Connections, as shown:
- Add a new connection by configuring the following details:
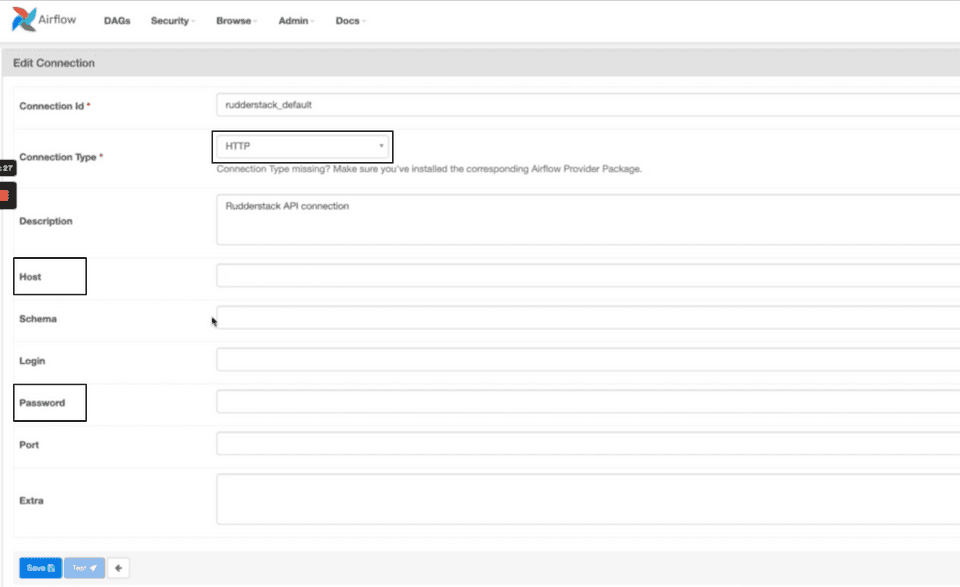
Connection ID: Specify a unique connection name.
RudderstackOperatorwill pick the connection with the namerudderstack_defaultby default. If you have created a connection with a different name, make sure that name is passed as a parameter toRudderstackOperator.Connection Type: For this field, select HTTP from the list.
Host: Set the value for this field to
https://api.rudderstack.com.Password: Enter your Personal Access Token here.
For more information on generating an access token, refer to the Personal Access Tokens guide.
Defining a DAG
Next, define a DAG with the tasks as per your requirement.
The following code snippet highlights an Airflow DAG with one task named rs_trigger_sync for the source ID 20dQV6yuUDUw31peWA8f7xxgHdN:
For more information on obtaining the source ID, refer to the FAQ section below.
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
from airflow import DAGfrom rudder_airflow_provider.operators.rudderstack import RudderstackOperator
default_args = { 'owner': 'airflow', 'depends_on_past': False, 'email': ['airflow@example.com'], 'email_on_failure': False}
with DAG( 'rudderstack-sample', default_args=default_args, description='A simple tutorial DAG', schedule_interval=timedelta(days=1), start_date=datetime(2021, 1, 1), catchup=False, tags=['rs']) as dag: rs_operator = RudderstackOperator( source_id='20dQV6yuUDUw31peWA8f7xxgHdN', connection_id='rudderstack_sync_conn', task_id='rs_trigger_sync' )For more information on where to find the source ID, refer to Sources guide.
Running the DAG
Once you have defined a DAG and configured an Airflow connection, run the following commands to allow Airflow to pick up and run the DAG:
export AIRFLOW_HOME=</path/to/airflow_home>mkdir $AIRFLOW_HOME/dagscp rudderstack_dag.py $AIRFLOW_HOME/dagsMake sure the Airflow scheduler is running in the background. Also, you must enable the DAG in the Airflow dashboard, as shown:
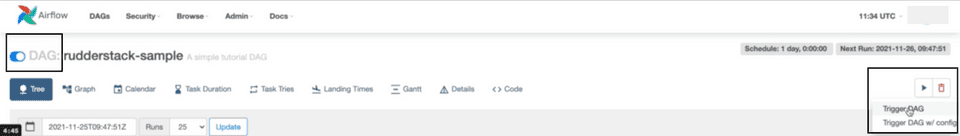
You can trigger a DAG by clicking on the play button on the right as seen above, and selecting Trigger DAG. Note that stopping the DAG will not cancel the ongoing sync.
FAQ
Where can I find the source ID for my Reverse ETL source?
The source ID is a unique identifier for any source set up in RudderStack.
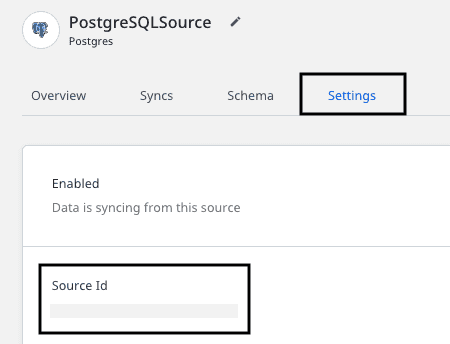
To obtain the source ID, go to the configured Reverse ETL source in your RudderStack dashboard and navigate to the Settings tab.
Contact us
For queries on any of the sections covered in this guide, you can contact us or start a conversation in our Slack community.