Connection Modes: Cloud Mode vs. Device Mode
Detailed technical description of the cloud and device modes for sending event data to your specified destinations.
This guide clarifies and details the differences between the two main RudderStack connection modes - cloud mode and device mode.
What are connection modes in RudderStack?
RudderStack's workflow is simple - it receives the event data from the sources and routes this data to the destinations. The connection modes determine how RudderStack tracks, transforms, and routes this event data.
There are two connection modes through which you can send your event data from your source apps to the desired destinations via RudderStack:
- Cloud mode
- Device mode
Cloud mode
In this mode, the SDK sends the event data directly to the RudderStack server. RudderStack then transforms this data and routes it to the desired destination. This transformation is done in the RudderStack backend, using RudderStack's Transformer module.
How cloud mode works
- The SDK sends the event data directly to the RudderStack server (backend).
- RudderStack transforms the events into a destination-specific format.
- The transformed events are then routed to the destination.
Suppose you want to analyze your website data in Google Analytics. To do so, you can use RudderStack's JavaScript SDK.
RudderStack defines a fixed event structure. If you track your events in this format, RudderStack takes care of transforming the events as required by Google Analytics. You can start by adding a JavaScript source and connecting it to the Google Analytics destination in your RudderStack dashboard.
Then, enable event tracking on your website by adding the JavaScript SDK snippet.
The SDK will automatically track and send the events to RudderStack. RudderStack then transforms this data into the required format and sends it to Google Analytics.
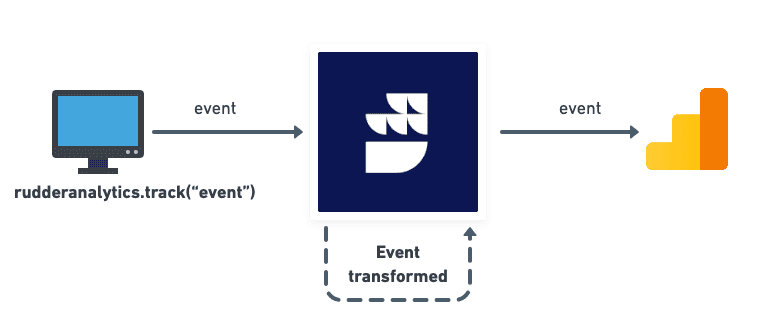
- RudderStack's warehouse destinations support sending data only through the cloud mode.
- All the RudderStack server-side SDKs support sending events only through cloud mode. This is because the server-side SDKs operate in the RudderStack backend and cannot load any additional destination-specific SDKs.
Device mode
In the device mode, RudderStack sends the event data to the destinations directly from your client (web or mobile app).
The RudderStack SDKs first load the native client libraries on your website or mobile app. These libraries allow RudderStack to use the data you collect on your device to call the destination APIs - without sending it to the RudderStack servers first.
How device mode works
Suppose you want to send your event data from your mobile app to Firebase via the RudderStack Android SDK (or any other mobile SDK). You can start by adding an Android source and connecting it to the Firebase destination in the RudderStack dashboard.
The RudderStack SDK will first download the Firebase SDK, transform the events natively, and then send them over to Firebase.

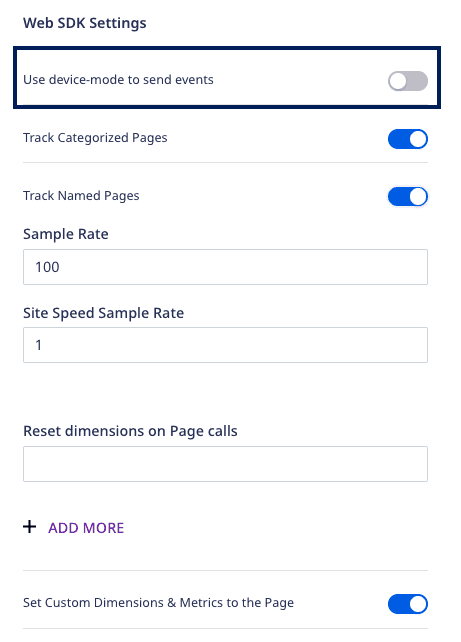
For some destinations, you can use the JavaScript SDK to send the events via the device mode. To do so, enable the Use native SDK to send events option under the destination-specific connection settings in the RudderStack dashboard, as shown:
FAQ
Which connection mode should I choose?
- Use the cloud mode if you wish to use the Transformations feature to transform your events before sending them to the destination.
- If you are planning to work with the destinations that record information directly on your users' devices, you should send the events via the device mode. There is a possibility that these destinations might not function correctly if they are not loaded directly on the device.
How to check which connection mode is supported by the destination?
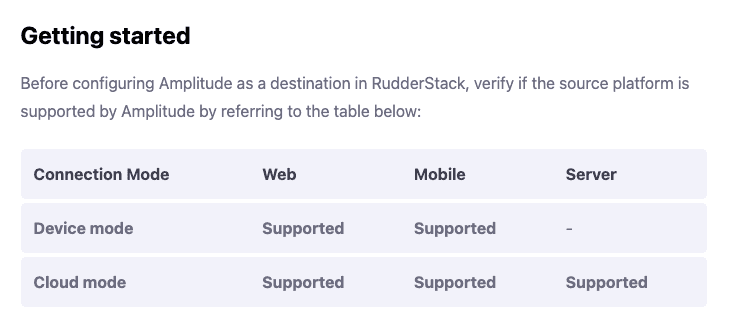
The easiest way to check the connection mode supported by the destination is to go refer to the individual destination's documentation.
The supported connection modes are mentioned for every destination in the Getting Started section of their respective documentation, as seen below:
Some RudderStack destinations support sending events via both the cloud and device mode. Some examples include:
What are the benefits of using the cloud mode to send events to the destination?
In the cloud mode, the event data is sent from the sources directly to the RudderStack server. RudderStack takes care of the event transformation and ensuring the format matches the destination's requirements. Since this transformation happens in the RudderStack server itself, your page size as well as the load times are not affected at all.
Contact us
For queries on any of the sections covered in this guide, you can contact us or start a conversation in our Slack community.