Amazon Redshift
Step-by-step guide to ingest your data from Amazon Redshift into RudderStack.
Amazon Redshift is one of the fastest cloud data warehouse services. It allows you to handle large analytical workloads with best-in-class performance, speed, and efficiency.
RudderStack supports Amazon Redshift as a source from which you can ingest data and route it to your desired downstream destinations.
Granting permissions
RudderStack requires you to grant certain user permissions on your Amazon Redshift warehouse to successfully access data from it.
Run the queries listed in the following sections on Amazon Redshift Console in the exact order to grant these permissions:
Step 1: Creating a new user in Redshift
- Create a new user
rudderwith a password<strong_unique_password>.
CREATE USER rudder WITH PASSWORD '<strong_unique_password>'Password considerations for Redshift
The password set in the above command must meet the following conditions:
- It should be 8-64 characters in length.
- It must contain atleast one upper case, one lower case, and one number.
- It can contain any ASCII characters with the ASCII codes 33-126, with the exception of
'(single quotation mark),"(double quotation mark),\,/, and@.
For more information on the password rules, refer to Amazon Redshift documentation.
Step 2: Creating the RudderStack schema and granting permissions
- Create a dedicated schema
_rudderstack.
CREATE SCHEMA "_rudderstack";The _rudderstack schema is used by RudderStack for storing the state of each data sync. Hence, its name should not be changed.
- Grant full access to schema
_rudderstackfor the userrudder.
GRANT ALL ON SCHEMA "_rudderstack" TO rudder;- Grant full access to the user
rudderover all the_rudderstackschema objects.
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON ALL TABLES IN SCHEMA "_rudderstack" TO rudder;Step 3: Granting permissions on your schema and table
- Grant access to the user
rudderto look up the objects within your schema<YOUR_SCHEMA>.
GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA "<YOUR_SCHEMA>" TO rudder;- Grant access to the user
rudderto read data from required table<YOUR_TABLE>.
GRANT SELECT ON TABLE "<YOUR_SCHEMA>"."<YOUR_TABLE>" TO rudder;Replace <YOUR_SCHEMA> and <YOUR_TABLE> with the exact names of your Redshift schema and table respectively.
Optional commands
- The following command grants access to the user
rudderto view and read data from all the tables present in the schema<YOUR_SCHEMA>:
GRANT SELECT ON ALL TABLES IN SCHEMA "<YOUR_SCHEMA>" TO rudder;Run the above command only if you're okay with RudderStack being able to access the data in all the tables residing within your specified schema.
- The following command grants access to the user
rudderto read data from all the future tables in the schema<YOUR_SCHEMA>:
ALTER DEFAULT PRIVILEGES IN SCHEMA "<YOUR_SCHEMA>" GRANT SELECT ON TABLES TO rudder;Run the above command only if you're okay with RudderStack being able to access the data in all the future tables residing within your specified schema.
Replace <YOUR_SCHEMA> with the exact name of your Redshift schema.
Setting up the Redshift source in RudderStack
To set up Redshift as a source in RudderStack, follow these steps:
Naming the source
- Log into your RudderStack dashboard.
- From the left navigation bar, go to Source > New Source > Reverse ETL. Then, select Redshift, as shown:

- Assign a name to the source.
Configuring the connection credentials
- Choose the relevant option from Table or Model to use the source to sync data from either a warehouse table or a model.
For more information on the difference between the Table and Model options when creating a Reverse ETL source, refer to the FAQ section below.
- Enter the relevant settings in the Connection Credentials section as listed below:
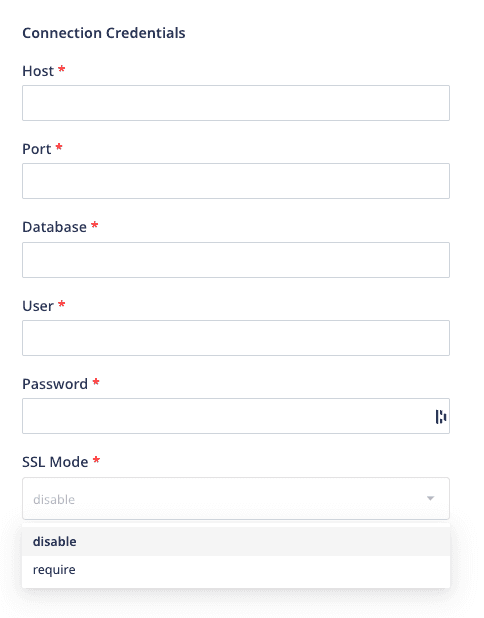
- Host - Host name of your Redshift service.
- Port - Port number of your Redshift service.
- Database - Database name in your Redshift instance where the data is loaded.
- User - Username which has the required read/write access to the above database.
- Password - Password for the above user.
- SSL Mode: Choose the SSL mode through which RudderStack will connect to your Redshift instance. RudderStack provides two options - disable and require. For more information on these options, refer to the FAQ section below.
If you've configured Redshift as a source before, you can select the existing credentials under the Use existing credentials option.
- Click on Continue to verify your credentials. RudderStack will then verify and validate your credentials.
For more information on these validation steps, refer to the FAQ section.
- Once verified, click on Continue to proceed.
Schedule settings
- Specify the Schedule Settings to schedule the data syncs from your Redshift instance.
RudderStack lets you schedule data syncs for your Reverse ETL sources and specify how and when the syncs will run. For more information on the Basic, CRON, and Manual schedule types, refer to the Sync Schedule Settings guide.
- After specifying the schedule type and run settings, click on Continue to finish the setup.
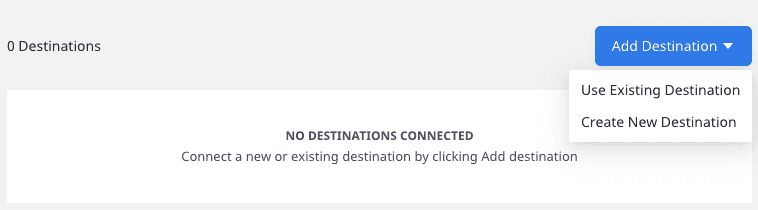
Redshift is now successfully configured as a source in your RudderStack dashboard. You can further connect this source to your preferred destination by clicking on Add Destination button, as shown:
Specifying the data to import
While connecting a destination to your Reverse ETL source, you can use the default JSON mapping or the Visual Data Mapping feature.
Based on the option(Table/Model) you chose while setting up the Reverse ETL source, follow the relevant guide for detailed steps:
FAQ
What are the SSL mode options when setting up the Redshift source in RudderStack?
When setting up a Redshift source, RudderStack provides the following two SSL options:
- disable: SSL mode is disabled when you select this option. Use it in cases where security is not an issue and you don't want any encryption overhead.
- require: When you select this option, your data is encrypted and sent to RudderStack. Use it in cases where security is important and you can deal with the resulting encryption overhead.
What do the three validations under Verifying Credentials imply?
When setting up a Reverse ETL source, once you proceed after entering the connection credentials, you will see the following three validations under the Verifying Credentials option:
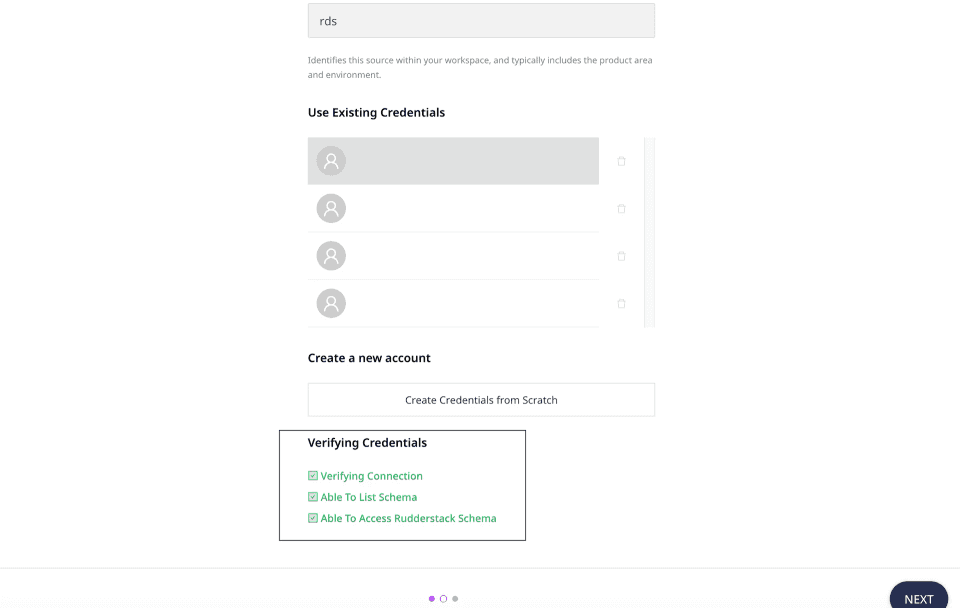
These options are explained below:
- Verifying Connection: This option indicates that RudderStack is trying to connect to the warehouse with the information specified in the connection credentials.
If this option gives an error, it means that one or more fields specified in the connection credentials are incorrect. Verify your credentials in this case.
- Able to List Schema: This option checks if RudderStack is able to fetch all the schema details using the provided credentials.
- Able to Access RudderStack Schema: This option implies that RudderStack is able to access the
_RUDDERSTACKschema you have created by successfully running all the commands in the User Permissions section.
If this option gives an error, verify if you have successfully created the _RUDDERSTACK schema and given RudderStack the required permissions to access it. For more information, refer to Creating the RudderStack schema and granting permissions section.
What is the difference between the Table and Model options when creating a Reverse ETL source?
When creating a new Reverse ETL source, you are presented with the following two options from which RudderStack will sync the data:
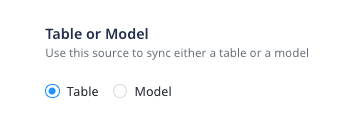
- When you choose Table, RudderStack imports all the data associated with the specified table during the sync.
- When you choose Model, RudderStack imports the data by running the query specified in the connected model, during the sync.
Contact us
For queries on any of the sections covered in this guide, you can contact us or start a conversation in our Slack community.