How to Add a Device Mode SDK to RudderStack JavaScript SDK
Detailed documentation to add a native SDK to RudderStack JavaScript SDK to enable native SDK support.
Connection Modes
There are two main modes of routing your event data to the required destinations:
- Cloud Mode: Our web and mobile SDKs provide APIs that can be called in case of events like
identify,page,screen,tracketc. The SDK formats the data and sends to the Data Plane. The Data Plane transforms the data, and routes the events to the destination. RudderStack Transformers transform the event payload to a destination-specific payload. ** - Device Mode: Another way to send events to the destinations is with their client libraries. RudderStack SDKs can initialize and transform the events, and call into the required destination APIs to route your events. These destination libraries once initialized can auto-track events without any explicit call from RudderStack. For example - the destination Hotjar, once initialized through RudderStack, starts capturing all forms of event data.
Destination Setup
Before adding a Device mode destination libraries to RudderStack JS, the corresponding destination should be added via the Control Plane.
The following screenshot demonstrates how to enable the native SDK to send events:
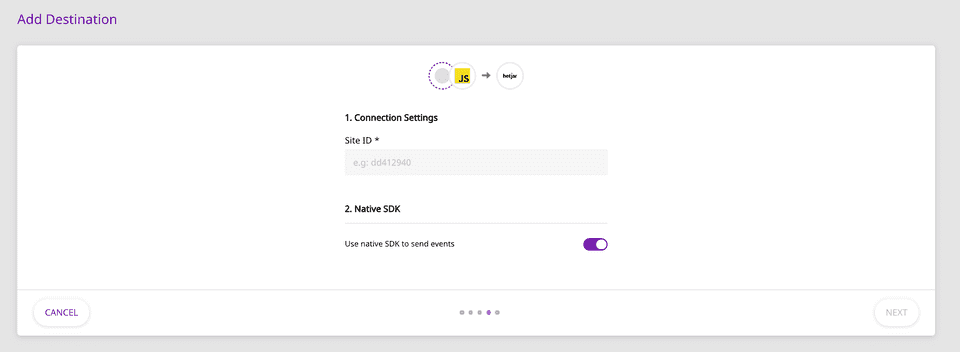 Move the Native SDK slider to enabled
Move the Native SDK slider to enabledSample Integration Template
class SampleIntegration { constructor(apiKey) { this.apiKey = apiKey // destination api key this.name = "SampleDestination" }
// Provides an iife for downloading and initializing the destination library/javascript // Once initialized, the destination object will be available for making a call and pushing event data init() {}
// rudderElement.message contains event data // Add custom implementation here identify(rudderElement) { // sd('set', 'userId', rudderElement.message.anonymous_id); }
// rudderElement.message contains event data // Add custom implementation here track(rudderElement) { // sd('send', 'event', rudderElement.message.event); }
// rudderElement.message contains event data // Add custom implementation here page(rudderElement) { // sd('set', 'page', rudderElement.properties.path); // sd ('send', 'pageview'); }
// Depend on the destination, where it enlists how to ensure if // the destination is ready isLoaded() { return !!window.sdplugins }}
export { SampleIntegration }Where to Add Your Integration
- Add your integration under https://github.com/rudderlabs/rudder-sdk-js/tree/master/integrations with the code as shown above in
browser.jsand anindex.jsfor exporting the integration. - Import the above integration in https://github.com/rudderlabs/rudder-sdk-js/blob/master/integrations/GA/index.js and add it to the exported list to be picked up by the base RudderStack SDK.
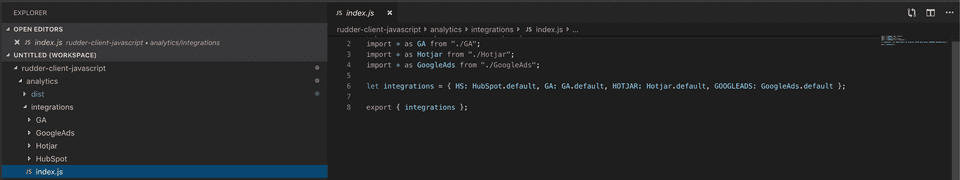 This exports the list of all native integrations
This exports the list of all native integrations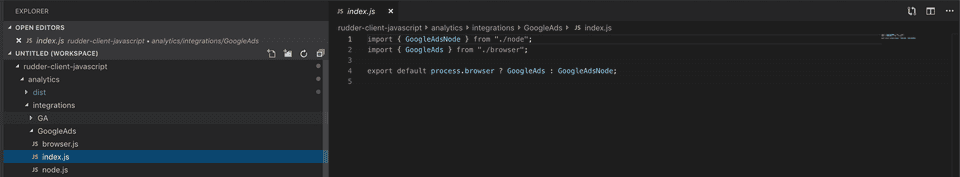 This exports the GoogleAds integration
This exports the GoogleAds integrationGet the config specific to your integration from the config object fetched by the base RudderStack SDK from the config plane and construct your integration object with the related configs.
Reference
We have a few native integrations already present in our JavaScript SDK. Please debug through them for any parameter references and call flow.
Below is a sample for Google Analytics native integration:
The following code implements the Google Analytics native integration under the file integrations/GA/browser.js:
// browser.js
import logger from "../../utils/logUtil"class GA { constructor(trackingID) { this.trackingID = trackingID //UA-1010101-1 this.name = "GA" }
init() { // iife that initailizes the destination
;(function (i, s, o, g, r, a, m) { i["GoogleAnalyticsObject"] = r ;(i[r] = i[r] || function () { ;(i[r].q = i[r].q || []).push(arguments) }), (i[r].l = 1 * new Date()) ;(a = s.createElement(o)), (m = s.getElementsByTagName(o)[0]) a.async = 1 a.src = g m.parentNode.insertBefore(a, m) })( window, document, "script", "https://www.google-analytics.com/analytics.js", "ga" )
//window.ga_debug = {trace: true};
ga("create", this.trackingID, "auto") ga("send", "pageview")
logger.debug("===in init GA===") }
identify(rudderElement) { ga("set", "userId", rudderElement.message.anonymous_id) logger.debug("in GoogleAnalyticsManager identify") }
track(rudderElement) { var eventCategory = rudderElement.message.event var eventAction = rudderElement.message.event var eventLabel = rudderElement.message.event var eventValue = "" if (rudderElement.message.properties) { eventValue = rudderElement.message.properties.value ? rudderElement.message.properties.value : rudderElement.message.properties.revenue }
var payLoad = { hitType: "event", eventCategory: eventCategory, eventAction: eventAction, eventLabel: eventLabel, eventValue: eventValue, } ga("send", "event", payLoad) logger.debug("in GoogleAnalyticsManager track") }
page(rudderElement) { logger.debug("in GoogleAnalyticsManager page") var path = rudderElement.properties && rudderElement.properties.path ? rudderElement.properties.path : undefined if (path) { ga("set", "page", path) } ga("send", "pageview") }
isLoaded() { logger.debug("in GA isLoaded") return !!window.gaplugins }}
export { GA }The following is the code for index.js under integrations/GA/index.js :
// index.js
// Ignore the node counter-part, we already have a seperate node sdk// that sends events directly to the data-plane (server-mode)
import { GANode } from "./node"import { GA } from "./browser"
export default process.browser ? GA : GANodeThe following is the code for adding the newly-added integration to the export list. The key name must be the same as the one configured in the config plane.
// root integrations/index.js
import * as HubSpot from "./HubSpot"import * as GA from "./GA"import * as Hotjar from "./Hotjar"import * as GoogleAds from "./GoogleAds"
// Note the key name is same as we have configured in our config-plane
let integrations = { HS: HubSpot.default, GA: GA.default, HOTJAR: Hotjar.default, GOOGLEADS: GoogleAds.default,}
export { integrations }Native Integration Methods
The native integrations should have the following methods for initializing the destination global object and forwarding event data.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
constructor | The RudderStack JavaScript SDK constructs an integration object with the destination config such as name, apiKey, custom mappings etc. fetched from your config plane. This information is required by the subsequent calls. |
isLoaded | This function is polled to check if the destination is ready |
init | Adds the destination script, i.e. the JavaScript snippet provided by the destination to initialize a global queue on window object. |
identify | RudderStack's JavaScript SDK calls this method to pass the identify event data. Destination-specific implementation can be added here. |
page | This method is called to pass the page event data. |
track | This method is called to pass the track event data. |
RudderStack JavaScript SDK makes a call to the config plane to fetch all native SDK-enabled destinations, before constructing and initializing the integration object with the fetched configuration. The isLoaded method should return true when the destination is ready to accept events.
Contact us
For queries on any of the sections covered in this guide, you can contact us or start a conversation in our Slack community.